endochondral bone is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous structure similar in shape to the resulting bone. In a long bone, ossification begins in the area that becomes the center of the shaft. In this area, cartilage cells become osteoblasts and start forming bone tissue. This process spreads toward either end of the bone. The only areas where cartilage is not soon replaced by bone tissue are the regions where the shaft joins the two epiphyses. These areas, called epiphyseal pla—res, are responsible for the bone's continuing growth in length. The bone's growth in diameter is due to the addition of layers of bone around the outside of the shaft. As they are formed, layers of bone on the inside of the shaft are removed. In all bones, the matrix is arranged in layers called lamellae. In compact bone, the lamellae are arranged concentrically around blood vessels, and the space containing each blood vessel is called a Haver—sian canal. The osteocytes are located between the lamellae, and the canaliculi containing their cellular extensions connect with the Haversian canals, allowing the passage of nutrients and other materials between the cells and the blood vessels. Bone tissue contains also many smaller blood vessels that extend from the periosteum and enter the bone through small openings. In long bones there is an additional blood supply, the nutrient artery, which represents the chief blood supply to the marrow. The structure of spongy is similar to that of compact bone. However, there are fewer Haversian canals, and the lamellae are arranged in a less regular fashion, forming spicules and strands known as trabeculae.
New words
bone – кость
internal – внешний
phosphorus – фосфор
atrophy – атрофия
spongy – губчатый
tendon – сухожилие
ligament – связка
flexible – гибкий
periosteum – надкостница
osteoblast – остеобласт (клетка, образующая кость)
rigidity – неподвижность
shape – форма
to crumble – крошиться
to congregate – собираться
epiphyseal – относящийся к эпифизу
shaft – ствол, тело (длинной) кости, диафиз
14. Skull
Bones of the skull: the neurocranium (the portion of the skull that surrounds and protects the brain) or the viscerocra—nium (i. e., the skeleton of the face). Bones of the neurocrani—um: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital, Ethmoid, Sphenoid.
Bones of the viscerocranium (surface): Maxilla, Nasal, Zy—gomatic, Mandible. Bones of the viscerocranium (deep): Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Vomer, Lacrimal, Palatine, Inferior nasal concha. Articulations: Most skull bones meet at immovable joints called sutures. The coronal suture is between the frontal and the parietal bones. The sagittal suture is between two parietal bones. The lambdoid suture is between the parietal and the occipital bones. The bregma is the point at which the coronal suture intersects the sagittal suture.
The lambda is the point at which the sagittal suture intersects the lambdoid suture. The pterion is the point on the lateral aspect of the skull where the greater wing of the sphenoid, parietal, frontal, and temporal bones converge. The temporomandibular joint is between the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone and the condylar process of the mandible.
The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands. Structures found within the substance of this gland include the following: Motor branches of the facial nerve. CN VII enters the parotid gland after emerging from the stylomastoid foramen at the base of the skull. Superficial temporal artery and vein. The artery is a terminal branch of the external carotid artery.
Retromandibular vein, which is formed from the maxillary and superficial temporal veins.
Great auricular nerve, which is a cutaneous branch of the cer vical plexus. Auriculotemporal nerve, which is a sensory branch of V3. It supplies the TMJ and conveys postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland. Parotid (Stensen's) duct, which enters the oral cavity at the level of the maxillary second molar. The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery in the neck. It terminates as the angular artery near the bridge of the nose.
The muscles of face
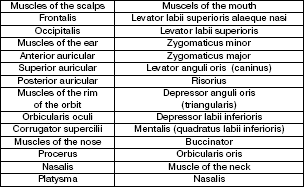
New words
brain – мозг
frontal – лобная
parietal – теменная
temporal – височная
occipital – затылочная
ethmoid – решетчатая
maxilla – верхняя челюсть
zygomatic – скуловой
mandible – нижняя челюсть
sphenoid – клиновидная
vomer – сошник
lacrimal – слезная
palatine – небная
nasal concha – носовая раковина
15. Neck. Cervical vertebrae, cartilages, triangels
Cervical vertebrae: There are seven cervical vertebrae of which the first two are atypical. All cervical vertebrae have the foramina transversaria which produce a canal that transmits the vertbral artery and vein.
Atlas: This is the first cervical vertebra (C1). It has no body and leaves a space to accommodate the dens of the second cervical vertebra. Axis: This is the second cervical vertebra (C2). It has odontoid process, which articulates with the atlas as a pivot joint. Hyoid bone is a small U—shaped bone, which is suspended by muscles and ligaments at the level of vertebra C3.
Laryngeal prominence is formed by the lamina of the thyroid cartilage.
Cricoid cartilage. The arch of the cricoid is palpable below the thyroid cartilage and superior to the first tracheal ring (vertebral level C6). Triangles of the neck: The neck is divided into a posterior and an arterior triangle by the sternocleidomastoid muscle. These triangles are subdivided by smaller muscles into six smaller triangles. Posterior triangle is bound by the sternocleidomastoid, the clavicle, and the trapezius. Occipital triangle is located above the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle. Its contents include the following: CN XI Cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus are the lesser occipital, great auricular, transverse cervical, and supaclavicular nerves.
Subclavian (omoclavicular, supraclavicular) triangle is located below the inferior belly of the omohyoid. Its contents include the following: Brachial plexus supraclavicu—lar portion The branches include the dorsal scapular, long thoracic, subclavius, and suprascapular nerves.
The third part of the subclavian artery enters the subclavian triangle.
The subclavian vein passes superficial to scalenus anterior muscle. It receives the external jugular vein.
Anterior triangle is bound by the sternocleidomastoid muse the midline of the neck, and the inferior border of the body of the mandible. Muscular triangle is bound by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and the midline of the neck. Carotid (vascular) triangle is bound by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. The carotid triangle contains the following: Internal jugular vein; Common carotid artery, bifurcates and form the internal and external carotid arteries. The external carotid artery has six branches (i. e., the superior thyroid; the ascending pharyngeal, the lingual, the facial, the occipital, and the posterior auricular arteries). Vagus nerve; hypoglossal nerve; internal and external laryngeal branches of the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. Digastric

