minutes to a few hours after swimming in an area where fragments of the cyanobacteria are suspended. Visible dermatitis and redness develop after 3 to 8 hours, followed by blisters and deep desquamation.
Measures: Washing of skin and eyes. Corticosteroid ointment. Antihistamine orally may be effective to relieve itching.
Reference : Mitchell/Rook; WHO Guidelines
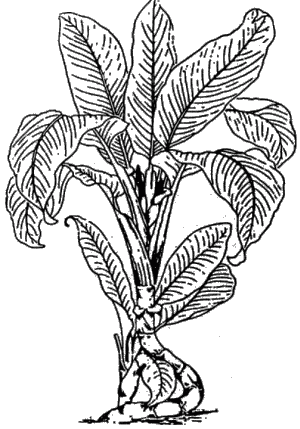
Dieffenbachia
genus or species
Synonyms: Dumb Cane (en), Dieffenbachie (de), Dieffenbachia (fr)
Occurrence: Home is tropical America in lowlands and damp areas. Popular indoor plant.
Description: Up to 1 m high plant with up to 25 cm long leaves with yellow pattern. Flourish butts of a yellow high sheet surround, blooms in March. It delivers a 'skunk-like' smell when cut.
Effects: Mechanical-chemical through calcium oxalate crystals (in connection with other materials) in all parts of this plant, particularly in the stem. Freshly cut parts are very skin irritating. After one day rashes develop. Irreversible skin damage is possible. When brought into the eye, the sap can cause injury of the cornea. All parts are very poisonous when ingested.
Measures: Washing of skin or eyes. Corticosteroid ointment, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference : Roth; Benezra; Dahlgren; Behl
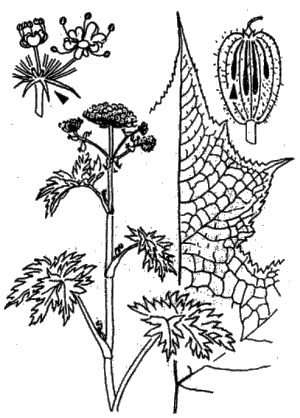
Giant Hogweed

genus or species
Synonyms: Parsnip Tree (en), Riesen-Barenklau (de), Herkuleskraut (de)
Occurrence: Home is the Caucasus. In Europe and North America frequently used as an ornamental plant in gardens and parks, also wild in woodlands and waysides. Widespread in Scandinavia.
Description: Perennial shrub, 3 to 5 m high, leaves up to 1 m long. White blossoms in clusters up to 50 cm in diameter. Stem hollow, with red speckles, up to 10 cm in diameter. Period of bloom from July to September.
Effects: Sap from all parts of the plant, particularly from the stem, acts as a phototoxic. When the juice gets on the skin and the skin is then exposed to ultraviolet light (some hours in the sun may be enough), the skin reddens next day, after another day a strong blistering can occur. The skin changes resemble second-degree burns. Often scars or pigment changes remain permanently or last for years. Also poisonous when ingested.
Measures: Avoid either the plant's sap or the sunlight. The sap can be washed away with water and soap. Corticosteroid ointment. See a doctor if necessary.
Reference: Benezra; Roth; 'Der Spiegel' Nr. 33/1989; 'JAMA' Dec 12/1980 Vol 244 No 23
Similar plants: Heracleum sphondylium (Cow Parsnip) is similar in appearance and effect, only up to 1.50 m in size, widespread in Europe. Similar plants include other Heracleum species as well as Pastinaca sativa and Angelica archangelica (also beloning to the Apiaceae family).
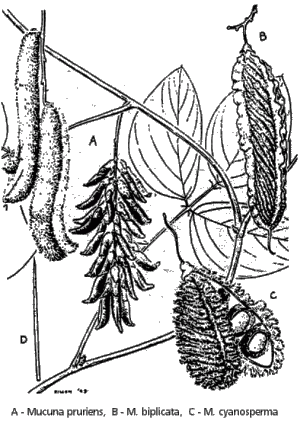
Cowhage

genus or species
Synonyms: Cow-Itch (en), Juckbohne (de)
Occurrence: Entire tropics in bushes and secondary forests.
Description: Creeper with whitish-greenish to purple or red inflorescences. Blossoms sometimes hairy. Pods 10 to 13 cm long, covered with approx. 5000 hairs which easily break off. The hairs on fruit and blossom are 1 to 2.5 mm long, have barbs and contain itch-producing Mucunain.
Effects: The hairs act as a mechanical-chemical skin-irritant. If only one of the hairs gets on the skin, itch can already be felt. Reddening of the skin and small papules or urticaria occur a few minutes after contact with the hairy parts of the plant. The hairs of Mucuna break off easily and can contaminate clothes or other objects. Dried parts of the plant remain active. There is no serious danger, except when the hairs get into the eye. In this case even blindness is likely.
Measures: To remove the hairs from the skin, adhesive tape and washing with water and soap are considered useful. Dermatitis can be treated with corticosteroid ointment. See a doctor immediately if hairs got into the eyes.
Reference: 'JAMA' Jan 17/1986 Vol 255 No 3; Merrill(1); Roth; Behl
Similar plants: The related species of Mucuna biplicata, M. cyanosperma, M. atropurpurea, M. gigantea, M. hirsuta, M. monosperma, M. nigricans. M. melanocarpa in Ethiopia. There are also harmless Mucuna species, however.
Indian Fig

genus or species
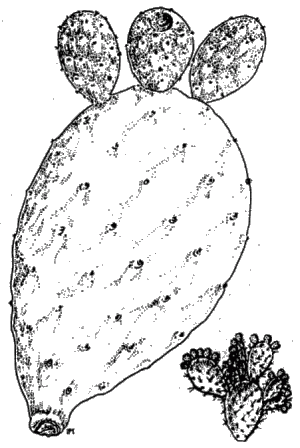
Synonyms: Sabra (en), Opuntie (de)
Occurrence: Approximately 200 species are native in tropical and subtropical America, also introduced to other continents. Frequently found in dry places. Also popular as a house plant.
Description: Cactuses in the form of shrubs or small trees with oval, flat segments and wide funnel-shaped yellow or red blossoms. Petals small, cylindrical, drop a short time after they appear. Opuntia can be an important survival plant in the desert: The egg-shaped fruits are edible uncooked when peeled. Clear potable water can be squeezed out of the segments. Peeled young segments are edible after cooking.
Effects: Mechanical, partly chemical. Most cactuses are armed with thorns, but Opuntia is among the most unpleasant ones because its fine thorns break off after the lightest touch and penetrate the skin easily. If dirt covers the plant, it can enter the skin with the thorns. Contact with the plant can result in papules and pigment changes which disappear after several months. The symptom is named Sabra Dermatitis and resembles

