Black Poison Wood

Metopium toxiferum Krug.

Synonyms: Poison Bark (en), Doctor's Gum (en)
Occurrence: West-Indies, Bahamas, Southern Florida, Yucatan, Belize, Cuba, Jamaica. Frequently found in open areas.
Description: Shrub or small tree up to 12 m tall, bark yellowish-brown, wide open branches. The 3- to 7-fold leaves are light green and up to 30 cm long, shiny on top and dull underneath. Blossoms white, berries yellow to orange. The latex sometimes emerges by itself from bark and leaves and becomes black when exposed to air.
Effects: Chemically skin-irritating and allergizing. After contact with the latex 70% of the Europeans develop itching papules a few days later which develop into blisters and remain for several weeks. The smoke of the burning wood is also skin-irritating.
Measures: Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Jackson; Dahlgren
Marking Nut Tree

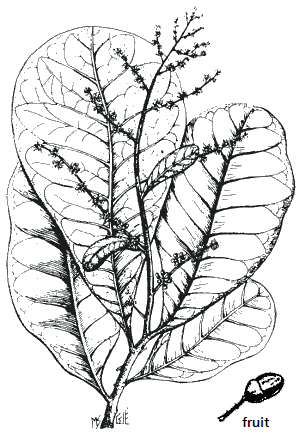
Synonyms: Bhilawa Tree (en), Kidney Bean of Malacca (en), Ostindischer Tintenbaum (de), Markfruchtbaum (de)
Other scientific names:
Occurrence: Resident in tropical India but also occasionally cultivated in other tropical countries. Growing wild in secondary forests and thickets.
Description: Deciduous tree up to 13 m tall with leathery, 20 to 60 cm long leaves. Blossoms yellowish-green, fruits black, 25 mm long. The fruit shell contains a black sap (ink), the pulp is orange, sweetish and reported to be edible.
Effects: The black sap of the fruit shell can cause itching a half day after contact and rashes and blistering within 24 hours. In Indian laundries the ink is sometimes used to mark clothes. In sensitive people these marks can also cause skin rashes after wearing the clothes, even after repeated laundering.
Measures: Cover blisters sterilely, apply corticosteroid ointment. Remove ink marks from clothes.
Reference: Roth; Behl; Benezra; Goldsmith
Ligas


Occurrence: In the Philippines and on the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia. Widespread in thickets at low altitudes.
Description: Shrub or small tree, 3 to 8 m high. Leaves 10 to 25 cm long. Blossoms whitish, 2 to 2.5 mm long, flowering in the Philippines from January to March. Stone fruit (drupe) 1 cm long, the upper part of the fruit is reddish, fleshy, and edible.
Effects: Very allergizing and skin-irritating. Dropping rain can cause skin rashes.
Measures: Cover blisters sterilely. Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Hanewald
Similar plants: Semecarpus forstenii and S. heterophylla on Sumatra and Java, named Rengas there, act similarly strong.
Rainbow Leaf


Synonyms: African Poison Ivy (en)
Occurrence: South Africa.
Description: Upright or climbing shrub or small deciduous tree up to 5 m tall. Twigs slim and smooth. Leaves alternate, on long stalks, divided into three parts, each of which are 10 to 12 cm long. Small blossoms in hairy panicles. Fruit flat and winged.
Effects: Allergizing. Some people react after contact with scattered skin rashes which are usually severe. Responsible for this is the sap of the plant.
Measures: Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention if necessary.
Reference: Benezra; Whiting
Rengas


Occurrence: Southern Burma.
Description: Evergreen tall hairless tree, flowering from December to March with lots of light yellow blossoms. Stone fruit (drupe) surrounded by violet petals.
Effects: Allergizing and chemically skin-irritating. The smoke of the burning wood can also be dangerous.
Measures: Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.

