Hughes was the first to send down a diver, who reported that Hughes’s net was wrapped around the hull of a wooden ship. Hughes, who knew the river’s history, thought that he might have found
The museum’s curator, Larry Gilmore, enlisted the support of a number of people, notably Mike Montieth, the Coast Guard commander of the “Cape D” station. An avid wreck diver himself, Montieth led a group of volunteers on a series of explorations of the wreck. In the murky darkness, Montieth began to sketch out the sloping sides of a wooden ship with a series of what looked like gun ports, a discovery that puzzled the investigators. Perhaps the hulk emerging from the sand wasn’t
To help resolve the questions, our National Park Service team was called in. The team leader, Daniel J. “Dan” Lenihan, who is an intensely focused, hardworking archeologist with a quiet demeanor, created the U.S. government’s first field team of underwater archeologists. The work of Dan and his team has also revolutionized underwater archeology in the United States, both in the way that work is done in the water and how archeologists think about shipwreck sites.
The team that assembles at Astoria in August 1987 includes Dan Lenihan, myself and another adjunct member of his team, Larry Nordby, who looks like a Viking and whose skill in the science of archeology is enhanced by the ability to measure and draw the remains of ships on the bottom in the worst possible conditions. We three are joined by volunteers — Mike Montieth, local shipwreck historian and wreck diver James Seeley White, and other local divers who have already been exploring the wreck of
As we gear up on the boats that are tied off the line that Mike has rigged to the wreck, he and Dan brief us. The wreck lies in only 48 feet of water on a hard sand bottom. That’s the easy part. The tough part is that the current rips through at such a fast pace that a diver can’t hold on when the tide ebbs and flows, so we can only go in the water at slack tide, when the current dies down to a dull roar. It’s also dark down there. Mud in the water near the surface blocks the light, so we have to feel our way over the broken wooden hulk, guided by a flashlight that illuminates just a few yards ahead. Then there are the fishing nets and crab pots caught on the ship’s protruding timbers, along with fishing line drifting in the current, to snag dive gear and unwary divers.
This is not going to be easy. In fact, I’m scared, but not enough to stay out of the water. We all jump in and make our way to the buoy that marks the wreck. The current tugs and pulls at us. Dan looks carefully at each one of us, checking to see if we’re ready. With a series of nods, we vent the air from our buoyancy compensating vests and start down the line, into the dark water.
The green water becomes gray and then black. Then, suddenly, I land on a thick wooden beam, encrusted with barnacles and wrapped with the buoy line. I’m on the wreck. Mike and the other divers have done an excellent job of sketching the basic outline of the wreck — the curving side of the hull, with ports open in what may be two rows. I turn and put my face close to the hull to examine it better, then switch on my light and follow Larry and Dan as we make a quick inspection of the hull. It is clearly half of a ship, with broken beams and timbers indicating where the decks were. From the weather deck to the bottom of the hull, this half is nearly complete, though we don’t yet know which side of the ship it is. Later dives will confirm that it is the starboard, or right-hand side, of the wreck.
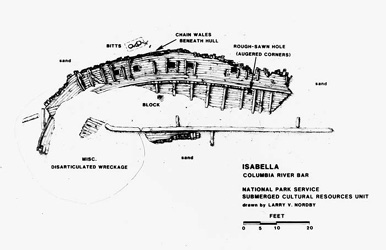
Dan has asked me to take a careful look at the ports to see if they are for guns. Six of them, in a row, line the hull below the level of the deck. They are small square ports — they seem too small to be for guns, I think — and I run my gloved hand along the top of one to check for hardware or the hole for a lanyard to pull open a gun port. The wood is solid, and there is no evidence of hinges or other hardware. They look to be cargo ports — square holes cut to load bulk cargo like coal or grain, then plugged with wood and caulked for the voyage. To make sure, I inspect each one. My reward for this meticulous work is a sudden encounter with the rotting head of a salmon, stuck in a wad of net inside one of the ports, its empty eye sockets staring at me as I stick my head into the port. It gives me a start, and I hit my head on the top of the narrow aperture and curse.
Dropping further down, I look for the second row of ports. I find only one opening, and after examining it closely, I decide that this is not a port. It is a roughly square hole that has been cut into the side of the ship. The rounded corners indicate that an auger was used to drill through the thick planks. The preservation of the wood, buried in sand and kept intact by the brackish water of the river where wood-eating organisms cannot survive, is remarkable; taking off my glove, I can feel the edges where a saw has bitten into the wood to cut out the hole. Some of the edges of the planks are splintered, as if an axe was used to help open up the hole. I smile, for this, I am sure, proves the wreck is
How do I know? The Hudson’s Bay Company kept
Dan is signaling that it’s time to surface. As we climb out, there are grins all around. This wreck, dark and dangerous as it is, is fascinating. The next few days quickly fall into a routine of early morning breakfasts at a small fishermen’s restaurant and two dives a day, which is all we can manage because of the currents and tides.
On one of these dives, I nearly become part of the wreck. Working in the darkness to map the wreck, Larry and I are signaled by Dan to get back to the line. The current has picked up slightly ahead of schedule, and we’ve got to surface. As we slowly work our way up the line, the current hits hard, and we have to hold on with both hands to fight the current to reach the boats. I’m the last one up. Exhausted, I stand on the ladder at the stern of Jim White’s boat. Forgetting my training, I pull off my mask and spit out my regulator. Instead of climbing up or handing up my weight belt or tank, I reach down and pull off my fins, one at a time. I fumble the last fin. As I reach out to catch it, the weight of my gear pulls me off the ladder and back into the water.
I fall fast and hit the bottom. Without my mask, I can’t see very well, but it looks like I’ve landed next to the wreck. The strong current is rolling me along the bottom, and I can’t reach my regulator, which has twisted and is now behind me. With the desperate strength people sometimes find in these situations, I push off the bottom with my legs and kick for the surface, my lungs burning. My outstretched hands hit the bottom of the boat, and I claw and scratch my way along the fiberglass hull to get out from under it. But the weight of my tank and belt drags me back down into the water. I hit the bottom again and start rolling. My mouth opens convulsively, and I take in a breath of cold water and gag. I’m going to die, I realize, and I’m really angry. Like most accidents, this one is a combination of a foolish move and a deceptively dangerous dive site. My eyes are wide open, but my vision is narrowing, and I know that I’m about to black out.
Finally, my dive training kicks in. I reach down and tug at the clasp of my weight belt. It falls free. Then I reach up to my buoyancy compensator to pull the lanyard that activates a co2 cartridge. I start to float off the river bed and remember not to hold my breath or I’ll burst my lungs as I rocket to the surface. When my head rises out of the water, I reach up and try to draw in a breath, choking with the water I’ve inhaled. Hands grab me and pull me into a Zodiac — I’ve rolled and drifted a few hundred yards away from where I fell in. I lie on the bottom of the inflatable, coughing up the muddy water from my lungs. Shaky, dripping and miserable, I climb onto the deck of Jim White’s boat, wipe my face, and ask, “Well, did I die like a man?” Dan makes sure I’m okay and debriefs me to ensure I learned from my mistake, and then we’re back at work at the next slack tide.
When everything is all done, we have a beautiful plan of the wreck, drawn by Larry, that confirms this is indeed

